Coronary Heart Disease and Immunoassay Testing
What is Coronary Heart Disease?
Coronary Heart Disease (CHD), also known as coronary artery disease, is a heart condition caused by the hardening and narrowing of the coronary arteries that supply blood to the heart. This leads to insufficient blood flow to the myocardium, causing symptoms such as chest pain, heart attacks, and heart failure. CHD is one of the most common cardiovascular diseases and a leading cause of death and disability.
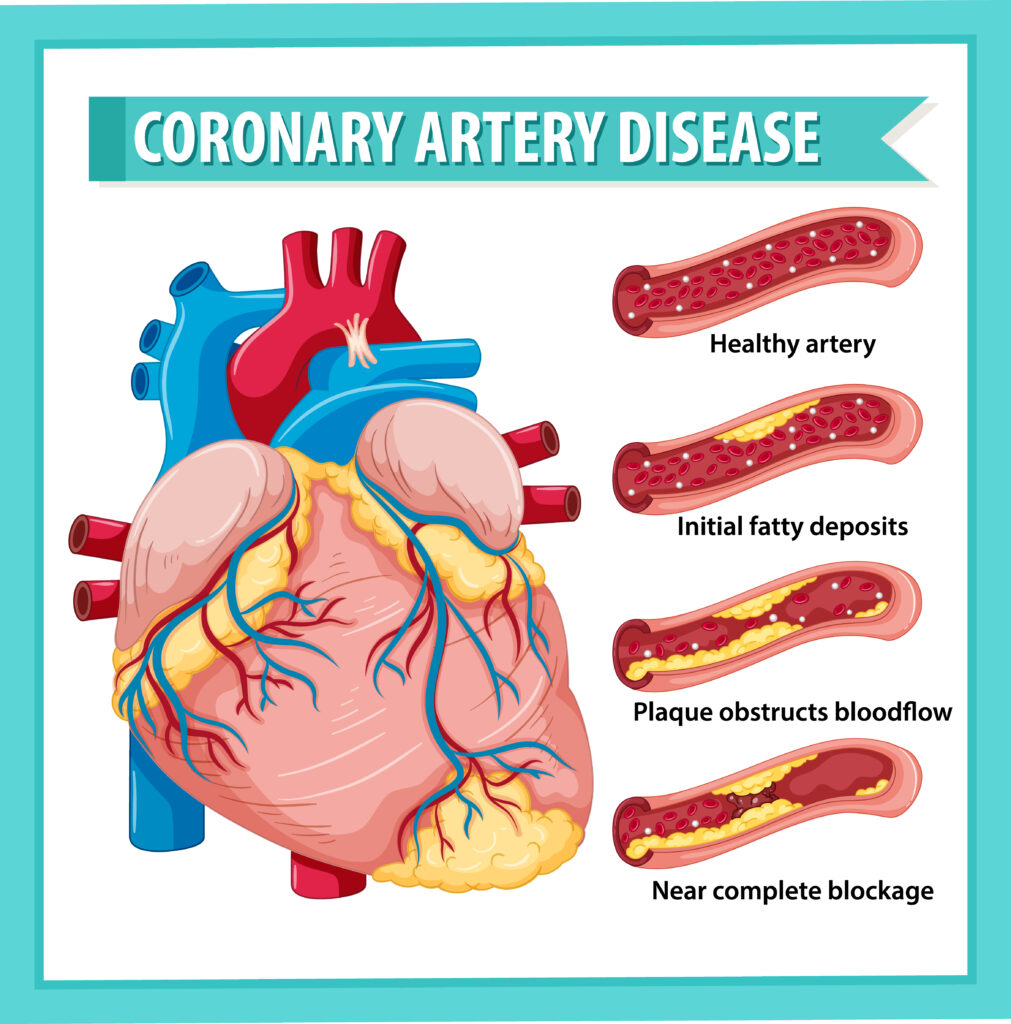
Causes of Coronary Heart Disease
The primary cause of CHD is atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the formation of lipid plaques within the arterial walls, leading to arterial narrowing and hardening. These plaques can rupture, causing the formation of blood clots that further obstruct blood flow, leading to conditions such as angina, myocardial infarction (heart attack), and heart failure.
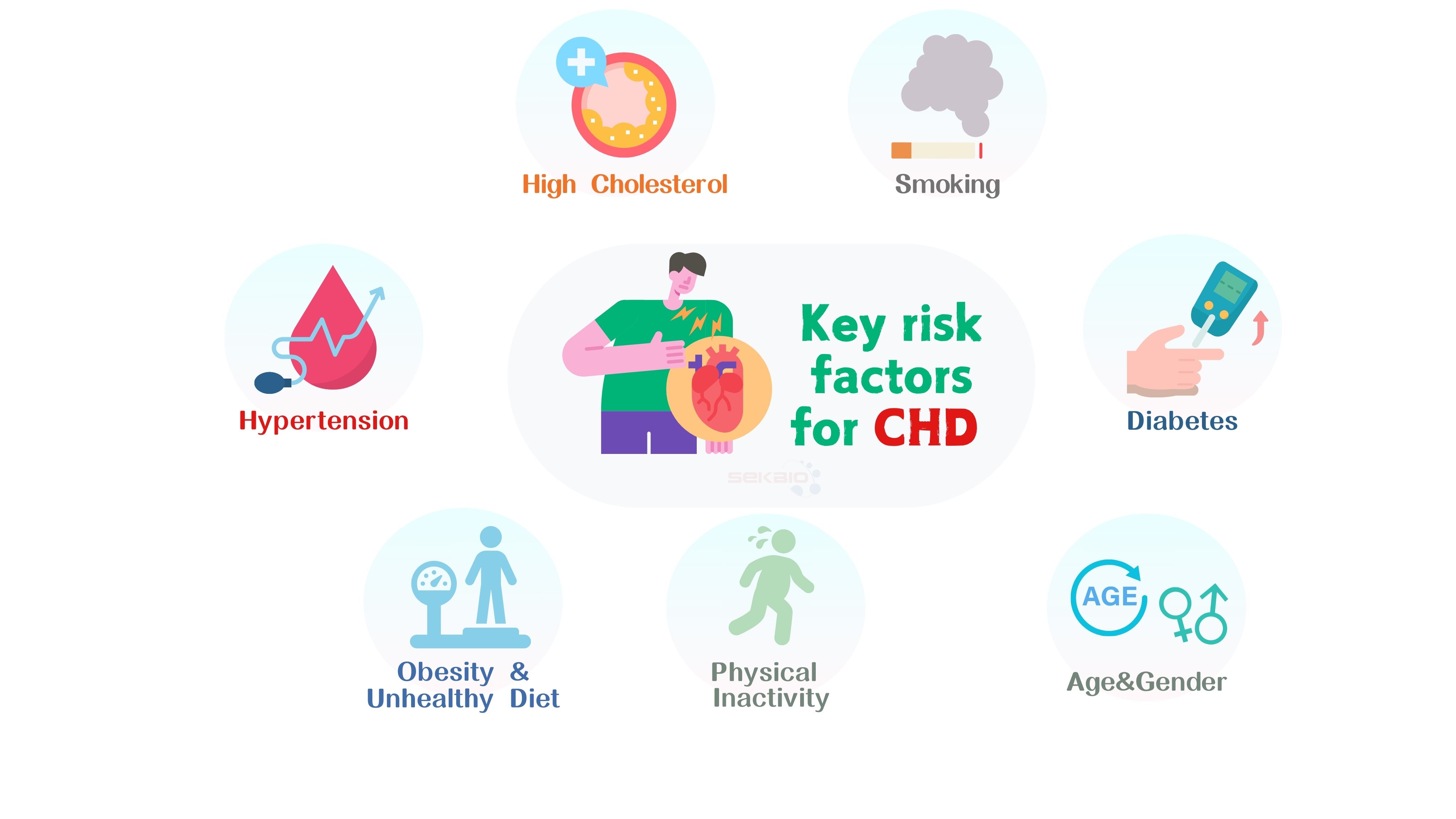
Key risk factors for CHD include:
Hypertension: Long-term high blood pressure can damage arterial walls, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis.
High Cholesterol: Elevated levels of cholesterol, particularly low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), contribute to plaque formation.
Smoking: Smoking damages the inner lining of arteries and accelerates the process of atherosclerosis.
Diabetes: High blood glucose levels in diabetes patients can damage blood vessels and increase atherosclerosis risk.
Obesity and Unhealthy Diet: Diets high in fat, salt, and sugar increase the risk of CHD.
Physical Inactivity: Lack of exercise leads to poor cardiovascular health and obesity.
Age and Gender: The risk of CHD increases with age, and it is higher in men and postmenopausal women.
Symptoms of Coronary Heart Disease
The primary symptom of CHD is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort often described as squeezing or pressure. This pain can radiate to the left shoulder, arm, neck, or jaw. Other symptoms include:
Chest Pain or Tightness: Worsens with physical activity or stress.
Shortness of Breath: Particularly during physical activity.
Fatigue: Feeling extremely tired even with minimal exertion.
Palpitations: Irregular or rapid heartbeat.
Syncope: Severe cases can lead to fainting or near-fainting episodes.
Prevention of Coronary Heart Disease
Preventing CHD involves managing risk factors through:
Healthy Diet: Choosing low-fat, low-salt, low-sugar foods, and consuming plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fish.
Regular Exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking, running, or swimming.
Smoking Cessation: Quitting smoking significantly reduces the risk of CHD.
Weight Control: Maintaining a healthy weight helps reduce the risk of hypertension, high cholesterol, and diabetes.
Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Control: Regular check-ups and medication if necessary to manage blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
Stress Management: Techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing help alleviate stress.
Diagnosis of Coronary Heart Disease
Diagnosing CHD involves a combination of symptoms, physical examination, and various tests, including:
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Records the electrical activity of the heart to detect ischemia or damage.
Echocardiogram: Uses ultrasound to examine heart structure and function.
Coronary Angiography: Involves injecting a contrast dye and taking X-ray images to view artery narrowing and blockages.
Blood Tests: Measure cholesterol, blood sugar, and other markers.
Role of Immunoassay Testing in Coronary Heart Disease
Immunoassay testing plays a crucial role in diagnosing and managing CHD by detecting specific biomarkers in the blood. These biomarkers help physicians assess the risk, diagnose the disease, and monitor treatment efficacy.
Common Immunoassay Markers for Coronary Heart Disease
1. C-Reactive Protein (CRP):
Significance: CRP is an inflammation marker, and elevated levels are associated with the development and progression of CHD.
Application: Used to assess cardiovascular risk and inflammation status.
2. Troponin:
Significance: Troponin is a specific marker of myocardial cell damage, and elevated levels indicate myocardial infarction.
Application: Used for the diagnosis of acute coronary syndromes such as myocardial infarction.
3. Lipoprotein-Associated Phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2):
Significance: Lp-PLA2 is associated with plaque stability in atherosclerosis. Elevated levels indicate plaque vulnerability and increased cardiovascular event risk.
Application: Used to evaluate the vulnerability of atherosclerotic plaques and cardiovascular risk.
4. B-Type Natriuretic Peptide (BNP) and N-Terminal Pro-BNP (NT-proBNP):
Significance: These markers are associated with heart failure. Elevated levels indicate an increased risk of heart failure.
Application: Used to assess the severity and prognosis of heart failure.
SEKBIO’s Immunoassay Products
SEKBIO offers a range of efficient and accurate immunoassay testing products for detecting CHD-related biomarkers. These products use advanced fluorescence chromatography immunoassay technology, providing high sensitivity, specificity, and ease of use. SEKBIO’s immunoassay products include:
CRP Rapid Test Kits: For inflammation and cardiovascular risk assessment.
BNP and NT-proBNP Test Kits: For assessing and monitoring heart failure.
Treatment of Coronary Heart Disease
Treatment options for CHD include medication, interventional procedures, and surgery:
Medication: Includes antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), statins, beta-blockers, and nitrates.
Interventional Procedures: Coronary stent placement to restore blood flow in narrowed arteries.
Surgery: Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) involves grafting vessels to bypass blocked coronary arteries, improving blood supply to the heart.
Conclusion
Coronary Heart Disease is a serious but preventable and manageable condition. By adopting a healthy lifestyle and undergoing regular check-ups, individuals can reduce their risk of CHD and maintain heart health. Early detection and proactive treatment significantly improve quality of life and longevity. Immunoassay testing plays a vital role in diagnosing and managing CHD. SEKBIO is committed to providing high-quality immunoassay products, assisting healthcare professionals in accurately diagnosing and managing CHD, and ensuring better health outcomes for patients.
















