World Thrombosis Day: Emphasizing Thrombosis Health and Interpreting the Clinical Value of FDP Testing
On this World Thrombosis Day, October 13, we call for greater understanding and attention to thrombosis, promoting standardized diagnosis and treatment. Thrombosis is one of the core causes behind the three major cardiovascular diseases globally (heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism). Every year, thrombus-related diseases lead to millions of deaths and serious disabilities, yet many people lack awareness of the risks and prevention methods.
What is Thrombosis?
Thrombosis is an abnormal blood clot formed within a blood vessel, obstructing normal blood flow and potentially leading to serious complications. Arterial thrombosis can result in heart attacks or strokes, while venous thrombosis can develop into deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolism (PE). The mortality and disability rates of these diseases are extremely high, particularly venous thromboembolism, which is the third most common cardiovascular disease worldwide.
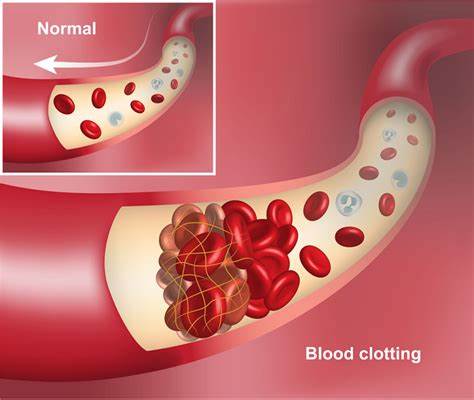
Common Risk Factors for Thrombosis
1. Prolonged Inactivity: Extended periods of inactivity can slow blood flow and increase the likelihood of thrombosis. Whether during long flights or sitting in the office, lack of movement increases the risk of lower limb venous thrombosis.
2. Surgery or Trauma: Major surgeries, especially hip and knee surgeries or cancer surgeries, increase the risk of venous thrombosis. The extended recovery period after surgery is also a dangerous phase.
3. Chronic Diseases: Patients with chronic conditions such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, or those undergoing hormone therapy or chemotherapy, have a significantly elevated risk of thrombosis.
4. Obesity and Smoking: Obesity slows blood flow, while smoking causes vascular damage, increasing the occurrence of thrombosis.
5. Pregnancy and Postpartum: Women experience a significant increase in thrombosis risk during pregnancy, especially postpartum, due to hormonal changes and increased blood volume.
6. Family History: If someone in your family has had thrombotic diseases, your risk of thrombosis increases accordingly.

Common Symptoms of Thrombosis
Understanding the early symptoms of thrombosis helps in timely detection and treatment. The following are symptoms associated with two major types of thrombotic diseases:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Commonly occurs in the legs, with symptoms including swelling, pain, warmth, redness or blue discoloration in the leg, and worsening pain when standing or walking. If left untreated, the clot may dislodge and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism.
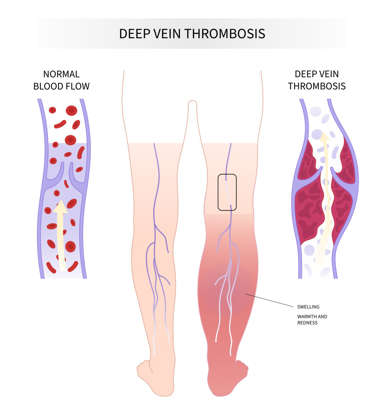
- Pulmonary Embolism (PE): Symptoms include chest pain, shortness of breath, rapid heartbeat, coughing up blood, or sudden fainting, which can be life-threatening.

The Key Role of FDP in Thrombosis Diagnosis
In addressing the prevention and treatment of thrombosis, FDP (Fibrin Degradation Products) testing is an important diagnostic tool for thrombotic diseases. FDPs are products generated from the breakdown of fibrin or fibrinogen under the action of plasmin, reflecting the process of thrombosis formation and fibrinolysis in the body. Testing FDP levels can help healthcare professionals detect early signs of thrombosis formation and dissolution, particularly in the diagnosis of venous thromboembolism (VTE) and disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC).
Clinical Significance of FDP:
- Monitoring Thrombosis Formation and Dissolution: Elevated FDP levels indicate potential thrombotic risks when thrombosis occurs.
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC): Significantly elevated FDP levels are a crucial marker for DIC, and FDP testing can help early identification of this serious condition.
- Post-Surgery and Trauma Monitoring: FDP testing post-surgery or trauma helps monitor the risk of thrombosis and prevent complications.
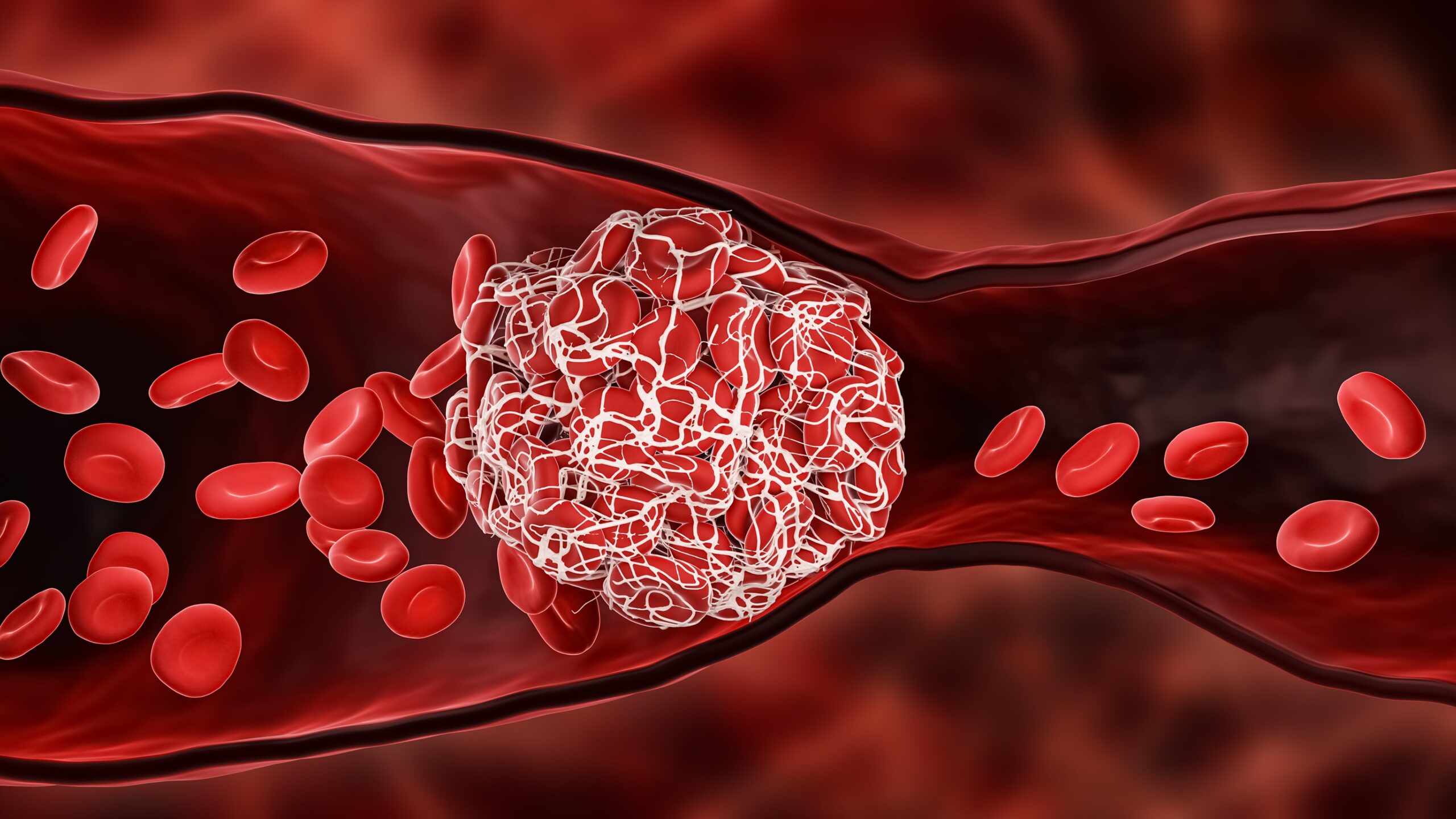
How to Prevent Thrombosis
1. Stay Active: When sitting for long periods, it's recommended to stand up and move around periodically, stretching limbs to aid blood circulation. Sedentary individuals can try simple movements like foot raises or leg extensions to maintain blood flow.
2. Healthy Diet: Consuming foods rich in dietary fiber and low in salt and fat helps reduce blood viscosity. Maintaining an ideal weight helps avoid obesity-related thrombotic risks.
3. Regular Check-ups: High-risk individuals, especially those with a family history of thrombosis or chronic diseases, should undergo regular screening and assessments for thrombotic risks to detect potential issues early.
4. Anticoagulation Therapy: For diagnosed thrombosis patients, anticoagulants such as heparin, warfarin, or DOACs (Direct Oral Anticoagulants) are key treatment methods. Proper use under medical guidance can significantly reduce recurrence and complications.
5. Wear Compression Stockings: Patients who are bedridden or sitting for long periods can wear medical compression stockings to help prevent venous thrombosis.
The Importance of Standardized Diagnosis and Treatment of Thrombosis
Although thrombosis is a preventable disease, the number of deaths caused by late diagnosis or treatment of thrombosis remains high globally each year. Standardized diagnosis and treatment are key to effectively reducing the burden of thrombotic diseases. On this World Thrombosis Day, SEKBIO calls on everyone to pay attention to the prevention and treatment of thrombosis. By promoting the critical role of FDP testing in thrombosis prevention and treatment, standardizing diagnosis and treatment, and innovating testing methods, we can help healthcare professionals make proactive and efficient decisions in thrombus prevention and control, improve patient outcomes, and help more people stay healthy and free from disease threats.
Starting today, focus on thrombosis and prioritize your health!
















